Vol 68, No 5 (2023)
- Year: 2023
- Published: 07.11.2023
- Articles: 12
- URL: https://virusjour.crie.ru/jour/issue/view/130
Full Issue
REVIEWS
Global genetic diversity of measles virus (Paramyxoviridae: Morbillivirus: Morbillivirus hominis): historical aspects and current state
Abstract
Monitoring the circulation of the measles virus and studying its genetic diversity is an important component of the measles elimination program. A methodological approach to molecular genetic studies and their interpretation in the measles surveillance was developed in the early 2000s. During its development, clear areas of circulation of each genotype of the virus were identified, therefore, the determination of viruses’ genotypes was proposed to monitor circulation and identify transmission pathways. However, in the future, due to a significant decrease in the number of active genotypes, an approach based on sub-genotyping was proposed: determining not only the genotype of the virus, but also its genetic lineage/genetic variant. The Global Measles and Rubella Laboratory Network (GMRLN) systematically monitors the circulation of the measles virus at the sub-genotypic level, depositing the results in a specialized database MeaNS2. It is this database that is the most complete and reliable source of information about the genetic characteristic of measles viruses.
This review presents both historical information and the latest data on the global genetic diversity of the measles virus.
 361-371
361-371


Vaccines to prevent Ebola virus disease: current challenges and perspectives
Abstract
Relevance. Ebola virus disease (EVD) is an acute infectious disease with an extremely high case fatality rate reaching up to 90%. EVD has become widely known since 2014–2016, when outbreak in West Africa occurred and led to epidemic, which caused travel-related cases on the territory of other continents.
There are two vaccines against EVD, prequalified by WHO for emergency use, as well as a number of vaccines, approved by local regulators in certain countries. However, even with the availability of effective vaccines, the lack of data on immune correlates of protection and duration of protective immune response in humans and primates is limiting factor for effectively preventing the spread of EVD outbreaks.
Aims. This review highlights experience of use of EVD vaccines during outbreaks in endemic areas, summarizes data on vaccine immunogenicity in clinical trials, and discusses perspectives for further development and use of effective EVD vaccines.
 372-384
372-384


ORIGINAL RESEARCHES
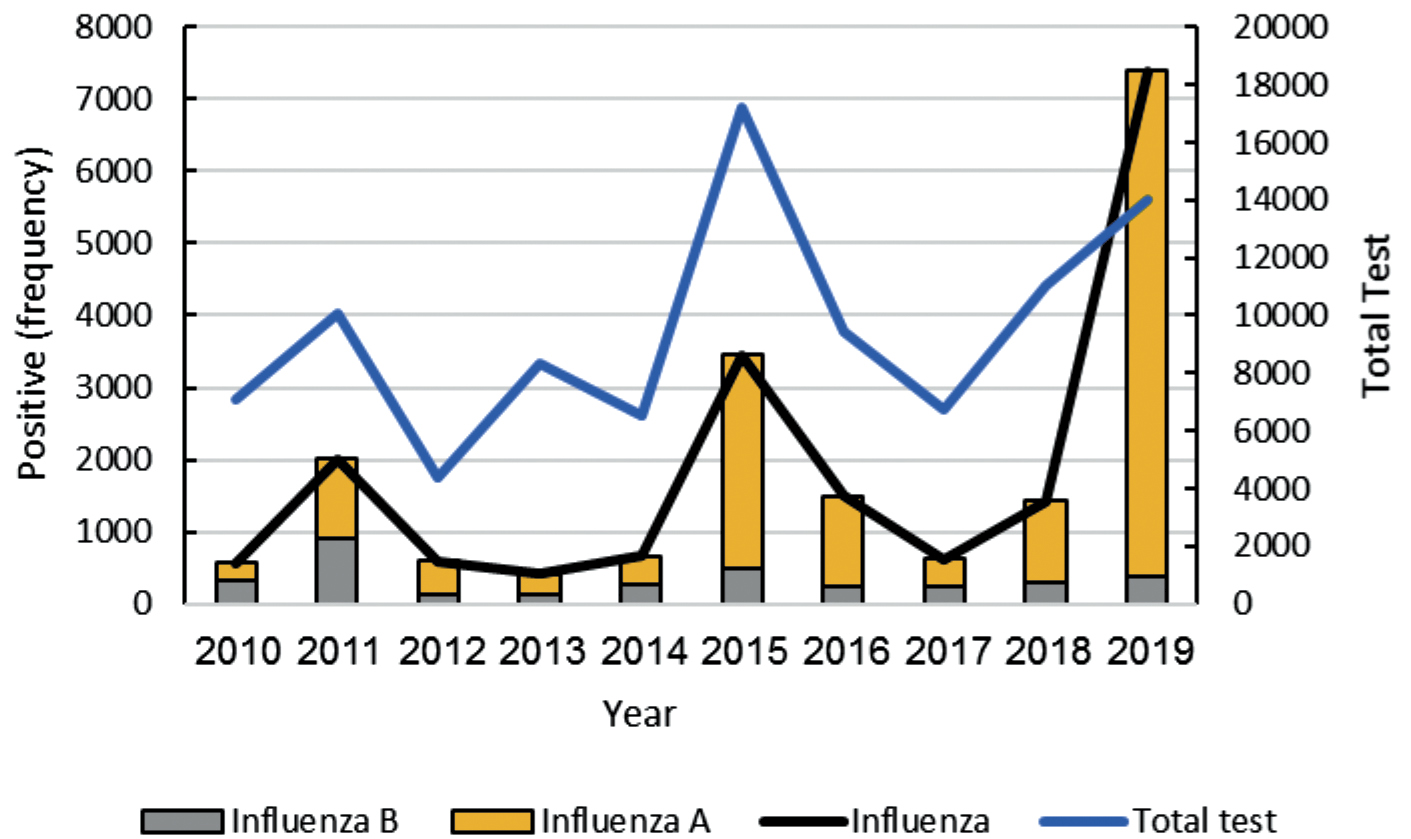
A decade genetic diversity in Circulating influenza B virus in Iran (2010–2019): Divergence from WHO-recommended vaccine strains
Abstract
Background. Data on the disease burden and circulation patterns of influenza B virus lineages for Iran are limited.
Objective. This review aims to describe the pattern of influenza B occurrence in Iran, comparing it with the proposed vaccine strains and determining the match and mismatch with the prescribed vaccine annually.
Methods. Various sources were used to retrieve information of the data; such as information from an online search of databases such as FluNet, GISAID, and NCBI. After extracting protein sequence records in GISAID, sequence alignment with vaccine strain and construction of a phylogenetic tree were performed. Subsequently, categories of the registered circulating strains were evaluated for matching with the vaccine strains.
Results. Of the total registered influenza-positive samples, 20.21% were related to influenza B virus. The phylogenic tree was designed based on 43 samples registered in the GISAID database; 76.74 and 23.25% sequences were of Yamagata and Victoria lineages, respectively. The most prevalent influenza B virus strains circulating during the study years belonged to the Yamagata lineage. In general, the match of the influenza B virus predominant circulating strains with administrated vaccines was observed in Iran. However, a high level of mismatch between the vaccine strain and Iranian isolates was identified in 2016‒2017.
Conclusion. The review of match and mismatch in influenza vaccine in order to improve the composition of the prescribed vaccine in each region is very important because the vaccine efficacy decreased when the strain included in vaccine did not match the circulating epidemic strain.
 385-393
385-393


Distribution of human gene polymorphisms allele frequencies associated with viral infections
Abstract
Introduction. The design of studies aimed at finding the association between the genetic factor and the studied feature (disease) involves a comparison of the ratio of genotypes or allelic proportions in the study group with those in the control group. At the stage of determining the ratio of genotypes of the studied polymorphisms in the reference group, researchers meet a number of problems, which are the subject of the present work.
Aim of the work is to provide scientific rationale for the feasibility of creating a national information system comprising genetic data of the relatively healthy population of Russia, incorporating its ethnic diversity.
Materials and methods. The study group, total 1020 people, was genotyped for a number of single nucleotide polymorphisms of human genes. A comparative characteristic of the frequency distribution of the studied polymorphisms with those presented in international databases as reference data was carried out using χ2 index.
Results. The frequency of SNP rs4986790 of the TLR4 gene significantly differs from the EUR population (p = 0.032) and the CEU subpopulation (p = 0.047). The allele frequencies of the rs1800795 (IL6) and rs1800896 (IL10) polymorphisms in the study population differ from the CEU subgroup (p = 0.030 and 0.012, respectively). The frequency of SNP rs2295119 (HLA-DPA2) in the study group is significantly different from the EUR population (p = 0.034).
Conclusion. The analysis carried out in this work confirms the need to create a domestic information system containing data on the occurrence of SNP alleles and genotypes for a conditionally healthy population and in subgroups with various pathological conditions.
 404-414
404-414


Study of the safety and immunogenicity of VLP-based vaccine for the prevention of rotavirus infection in neonatal minipig model
Abstract
Introduction. In Russia, almost half of the cases of acute intestinal infections of established etiology in 2022 are due to rotavirus infection (RVI). There is no specific treatment for rotavirus gastroenteritis. There is a need to develop modern, effective and safe vaccines to combat rotavirus infection that are not capable of multiplying (replicating) in the body of the vaccinated person. A promising approach is to create vaccines based on virus-like particles (VLPs).
Objective. Study of the safety and immunogenicity of a vaccine against rotavirus infection based on virus-like particles of human rotavirus A in newborn minipigs with multiple intramuscular administration.
Materials and methods. Newborn minipigs were used as an animal model in this study. The safety of the tested vaccine was assessed based on thermometry data, clinical examination, body weight gain, clinical and biochemical blood parameters, as well as necropsy and histological examination. When studying the immunogenic properties of the Gam-VLP-rota vaccine in doses of 30 and 120 µg, the cellular, humoral and secretory immune response was studied.
Results. The results of assessing the general condition of animals during the immunization period, data from clinical, laboratory and pathomorphological studies indicate the safety of the vaccine against human rotavirus infection based on VLP (Gam-VLP-rota) when administered three times intramuscularly. Good local tolerance of the tested vaccine was demonstrated. The results of the assessment of humoral immunity indicate the formation of a stable immune response after three-time immunization with Gam-VLP-rota, stimulation of the production of antigen-specific IgG antibodies and their functional activity to neutralize human rotavirus A. It was shown that following the triple immunization with the minimum tested concentration of 30 µg/dose, animals developed a cell-mediated immune response. The results of the IgA titer in blood serum and intestinal lavages indicate the formation of both a systemic immunological response and the formation of specific secretory immunity to human rotavirus A.
Conclusion. Thus, three-time intramuscular immunization of minipigs with the Gam-VLP-rota vaccine forms stable protective humoral and cellular immunity in experimental animals. Evaluated vaccine is safe and has good local tolerability.
 415-427
415-427


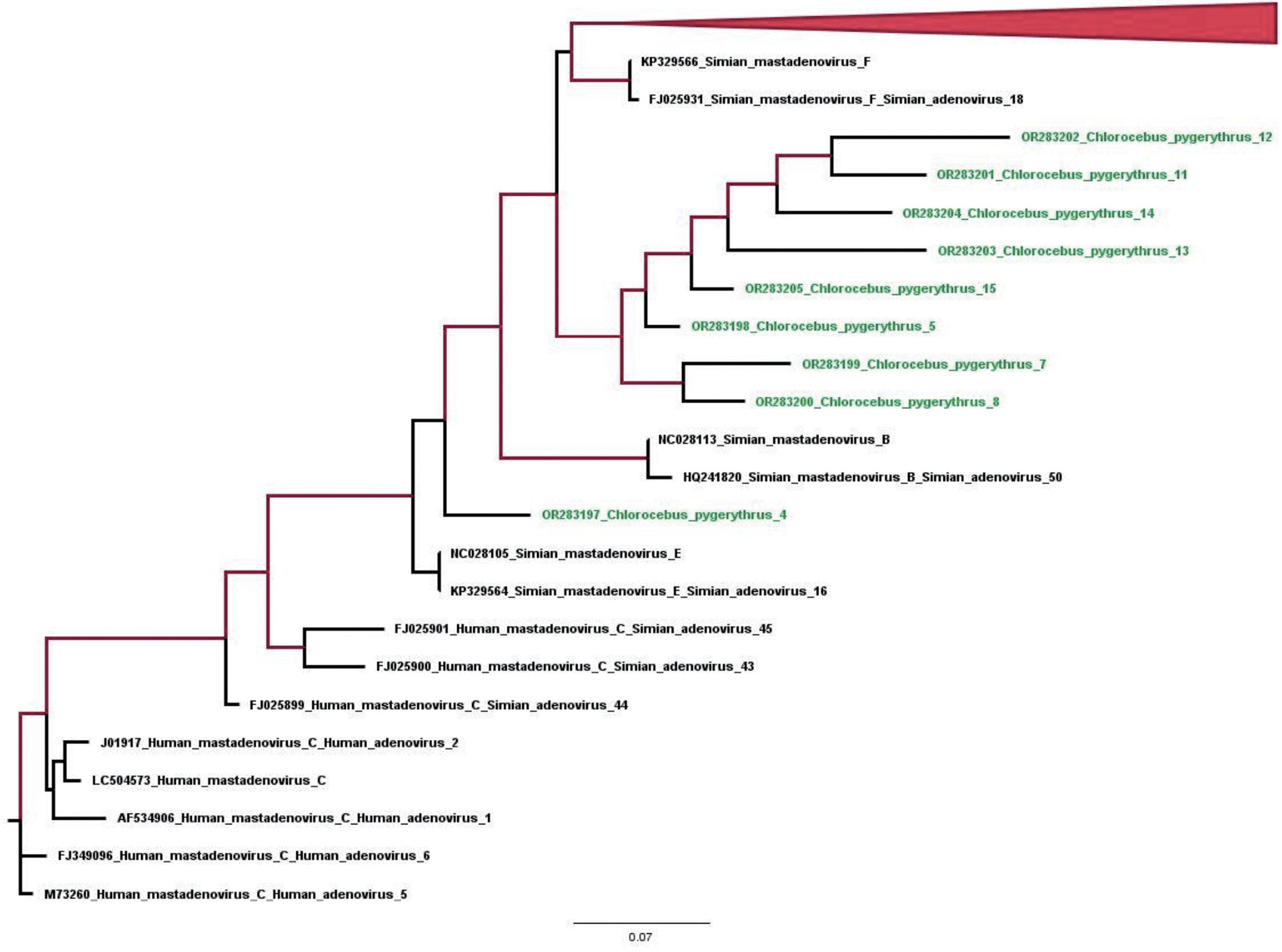
Markers of antroponotic viral infections in vervet monkeys arrived from their natural habitat (Tanzania)
Abstract
Introduction. Various human viruses have been identified in wild monkeys and in captive primates. Cases of transmission of viruses from wild monkeys to humans and vice versa are known.
The aim of this study was to identify markers of anthroponotic viral infections in vervet monkeys (Chlorocebus pygerythrus) arrived from their natural habitat (Tanzania).
Materials and methods. Fecal samples (n = 56) and blood serum samples (n = 75) obtained from 75 animals, respectively, on days 10 and 23 after admission to the primate center, were tested for the markers of anthroponotic viral infections (Ebola virus, Marburg virus, lymphocytic choriomeningitis, hepatitis C virus, herpes simplex virus (HSV), cytomegalovirus (CMV), Epstein–Barr virus (EBV), parainfluenza types 1 and 3, intestinal adenoviruses, rotaviruses) by enzyme immunoassay (ELISA) and polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
Results and discussion. Among the examined animals, markers of 6 out of 11 tested viral infections were identified. Detection rates of IgG antibodies to HSV-1,2 (15.9%) and CMV (15.9%) were two times as low as IgG antibodies to EBV (31.8%). Among the markers of respiratory viral infections, IgG antibodies to parainfluenza virus type 1 were found (6.8%). 14.3% of the animals had rotavirus antigen, and 94% had simian adenovirus DNA. Markers of hemorrhagic fevers Ebola, Marburg, LCM, hepatitis C, and type 3 parainfluenza were not detected.
Conclusion. When importing monkeys from different regions of the world, an expanded screening for viral infections is needed considering the epidemiological situation both in the country of importation and in the country of destination.
 394-403
394-403


The role of the encephalomyocarditis virus type 1 proteins L and 2A in the inhibition of the synthesis of cellular proteins and the accumulation of viral proteins during infection
Abstract
Introduction. Infection of cells with encephalomyocarditis virus type 1 (EMCV-1, Cardiovirus A: Picornaviridae) is accompanied by suppression of cellular protein synthesis. The main role in the inhibition of cellular translation is assigned to the L and 2A «security» proteins. The mechanism of the possible influence of the L protein on cellular translation is unknown. There are hypotheses about the mechanism of influence of 2A protein on the efficiency of cap-dependent translation, which are based on interaction with translation factors and ribosome subunits. However, the available experimental data are contradictory, obtained using different approaches, and do not form a unified model of the interaction between the L and 2A proteins and the cellular translation machinery.
Aim. To study the role of L and 2A «security» proteins in the suppression of translation of cellular proteins and the efficiency of translation and processing of viral proteins in infected cells.
Materials and methods. Mutant variants of EMCV-1 were obtained to study the properties of L and 2A viral proteins: Zfmut, which has a defective L; Δ2A encoding a partially deleted 2A; Zfmut&Δ2A containing mutations in both proteins. Translational processes in infected cells were studied by Western-blot and the pulse method of incorporating radioactively labeled amino acids (14C) into newly synthesized proteins, followed by radioautography.
Results. The functional inactivation of the 2A protein does not affect the inhibition of cellular protein synthesis. A direct correlation was found between the presence of active L protein and specific inactivation of cellular protein synthesis at an early stage of viral infection. Nonspecific suppression of the translational processes of the infected cell, accompanied by phosphorylation of eIF2α, occurs at the late stage of infection. Partial removal of the 2A protein from the EMCV-1 genome does not affect the development of this process, while inactivation of the L protein accelerates the onset of complete inhibition of protein synthesis. Partial deletion of the 2A disrupts the processing of viral capsid proteins. Suppression of L protein functions leads to a decrease in the efficiency of viral translation.
Conclusion. A study of the role of EMCV-1 L and 2A proteins during the translational processes of an infected cell, first performed using infectious viral pathogens lacking active L and 2A proteins in one experiment, showed that 2A protein is not implicated in the inhibition of cellular translation in HeLa cells; L protein seems to play an important role not only in the specific inhibition of cellular translation but also in maintaining the efficient synthesis of viral proteins; 2A protein is involved not only in primary but also in secondary processing of EMCV-1 capsid proteins.
 428-444
428-444


Association of polymorphic variants of hemostatic system genes with the course of COVID-19
Abstract
Introduction. COVID-19 is characterized by a varied clinical course.
The aim of the work was to identify associations of SNPs of hemostatic system genes with COVID-19.
Materials and methods. DNA was isolated from patients (n=117) and healthy participants (n=104). All infected patients were divided into 3 groups, depending on disease severity assessment, which was appreciated by NEWS2. Another group consisted of participants, who had asymptomatic infection in the past. Determination of SNPs of the genes FGB (-455 G/A), FII (20210 G/A), FV (1691 G/A), FVII (10976 G/A), FXIIIA1 (103 G/T), ITGA2 (807 C/T), ITGB3 (1565 T/C), SERPINE1 (-675 5G/4G) were performed by PCR using the “Genetics of Hemostasis” kit (“DNA-Technology”, Russia).
Results. In analyzed SNPs, no significant differences were detected between the group of infected patients and healthy participants. But significant association was revealed in gene SERPINE1 (-675 5G/4G), when patient groups, differing in the disease severity, were analyzed relative to the group of participants with asymptomatic infection (p=0.0381; p=0 .0066; p=0.0009). It was found, that as COVID-19 severity scores increased, the proportion of 5G allele of gene SERPINE1 decreased, and the proportion of the 4G allele increased (p=0.005; p=0.009; p=0.0005). Similar processes were observed for genotypes 5G/5G and 4G/4G.
Discussion. The gene SERPINE1 (-675 5G/4G) is associated with the severity of COVID-19.
Conclusion. For the first time, it was discovered that 5G/5G genotype of gene SERPINE1 (-675 5G/4G) can be a marker of a milder course of COVID-19, and the 4G/4G genotype as a more severe one.
 445-453
445-453


ANNIVERSARY DATES
To the 90th anniversary of the birth of Nikolai Veniaminovich Kaverin
Abstract
October 11, 2023 marked the 90th anniversary of the birth of the outstanding Russian virologist, academician of the Russian Academy of Sciences Nikolai Veniaminovich Kaverin. N.V.
Kaverin was born in Leningrad into the famous literary family of Veniamin Aleksandrovich Kaverin and Lydia Nikolaevna Tynyanova. In 1951 he graduated from school with a gold medal and entered the 1st Moscow Medical Institute named after. THEM. Sechenov. During his senior years, Kaverin already worked at the Research Institute of Virology named after. DI. Ivanovsky RAMS, and in 1960, upon completion of graduate school, defended his Ph.D. thesis.
 454-454
454-454


OBITUARY
Besednova Natalia Nikolaevna (02.02.1935 – 23.09.2023)
Abstract
Research Institute of Epidemiology and Microbiology named after. G.P. Somova of Rospotrebnadzor regrets to announce that on September 23, 2023, at the age of 89, Natalia Nikolaevna Besednova, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor, Honored Scientist of the Russian Federation, full member of the Russian Academy of Sciences, laureate of the USSR State Prize, outstanding scientist, brilliant organizer, excellent teacher and wonderful person.
 455-456
455-456


INFORMATION
 457-457
457-457


 458-458
458-458