Vol 70, No 4 (2025)
- Year: 2025
- Published: 16.09.2025
- Articles: 9
- URL: https://virusjour.crie.ru/jour/issue/view/141
Full Issue
REVIEWS
Occult hepatitis B: prevalence and clinical significance. Role in liver pathology and in viral coinfections
Abstract
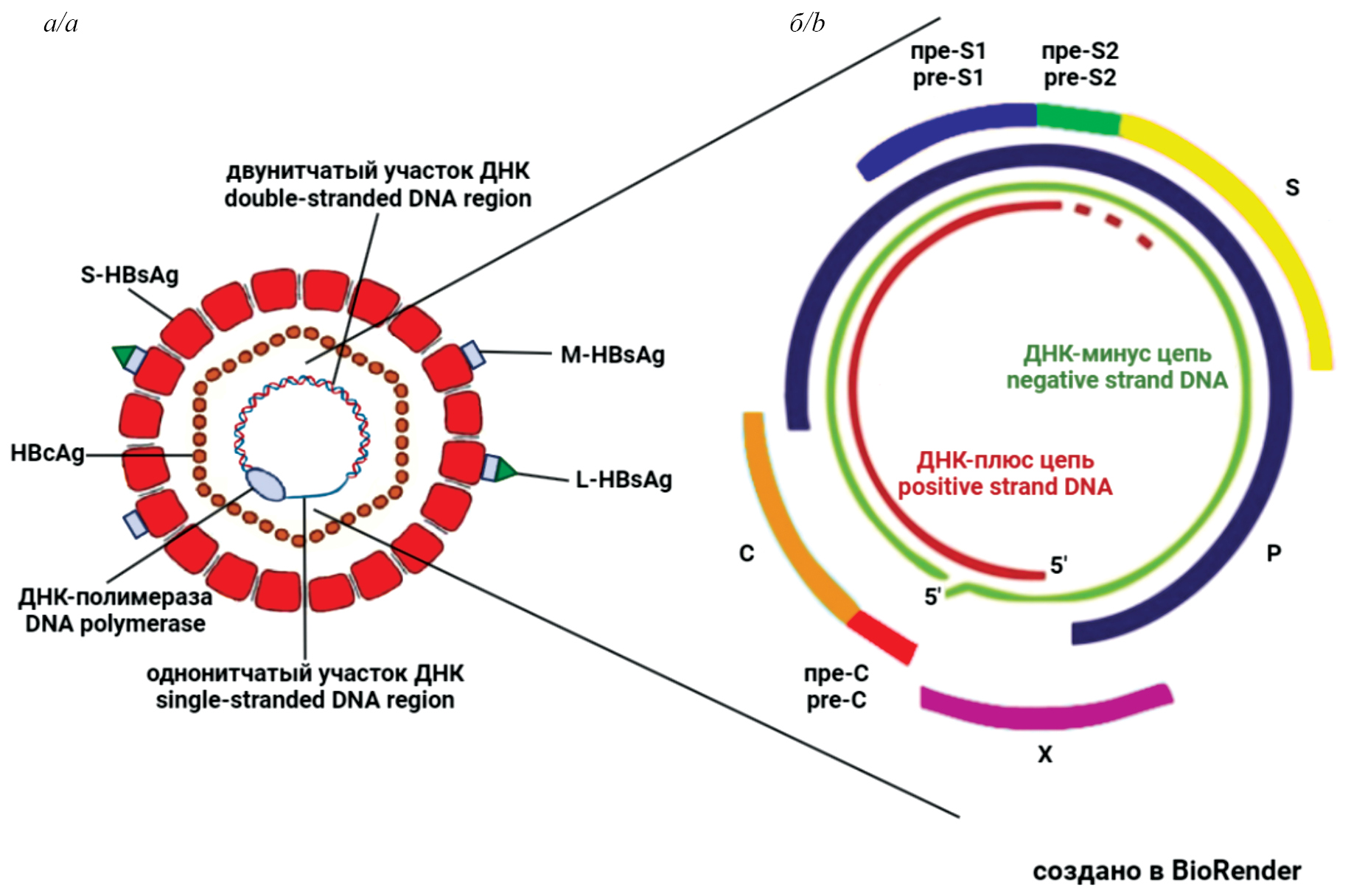
The review examines issues related to occult hepatitis B virus infection (OBI), which occurs at a late stage of chronic hepatitis B (CHB) after HBsAg clearance. In clinical practice, OBI is detected by the absence of HBsAg and the presence of antibodies to HBcAg in the blood serum and is often referred to as «past» or «resolved» hepatitis B. However, hepatitis B virus (HBV) DNA remains in liver cells, is poorly detected by routine diagnostic methods, and cannot be removed by existing therapies. Data on the prevalence of OBI vary, but it is found in all regions of the world, much more often in regions with a high prevalence of HBV. Data on the association of OBI with fibrosis, cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) have been obtained. It has been established that OBI is associated with an increased risk of HBV reactivation in patients with infections with other viruses, as well as in cancer patients whose treatment includes immunosuppressive therapy. HBV reactivation leads to severe consequences and, in the absence of treatment, death of patients. It can be concluded that to achieve the goal set by WHO for the eradication of viral hepatitis by 2030, it is necessary to solve the problem of OBI. In order to make this possible, it is essential to create new, more sensitive and informative diagnostic tests, effective methods of HBV DNA elimination, and to investigate the mechanisms of OBI development in more depth.
 299-316
299-316


Zika virus in the shadows: an underrecognized contributor to Nigeria’s febrile disease landscape
Abstract
Background. Zika virus (Orthoflavivirus zikaense), a mosquito-borne virus in the family Flaviviridae and genus Orthoflavivirus, has garnered international attention due to its neurological and congenital impacts. Although endemic to Africa, its presence in Nigeria remains poorly understood and often overshadowed by other febrile illnesses such as malaria and dengue. This review synthesizes peer-reviewed literature published between 2015 and 2025 to explore the epidemiology, diagnostic challenges, and public health implications of ZIKV in Nigeria.
Materials and methods. A narrative synthesis of studies reporting ZIKV infection in Nigeria was conducted using targeted searches of PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, and African Journals Online. Eligible studies included peer-reviewed articles in English reporting serological or molecular data from human or vector populations.
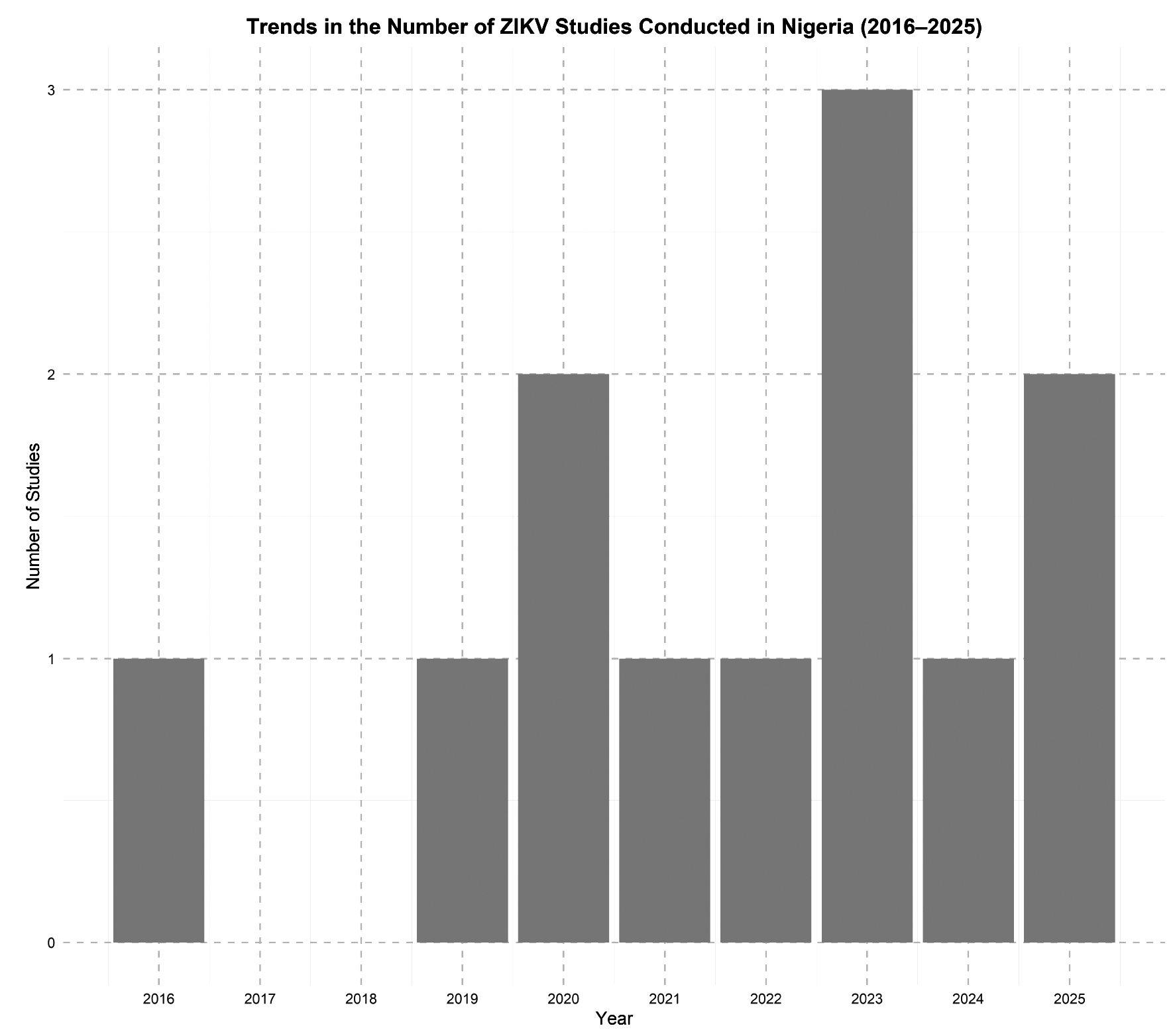
Results. Evidence from eleven studies across ten states shows seroprevalence of ZIKV ranging from 1.4% to over 50%, particularly among pregnant women and febrile patients. Diagnostic gaps, including symptom overlap and serological cross-reactivity, contribute to underreporting. Co-endemicity with other arboviruses and limited surveillance further obscure ZIKV’s public health impact.
Conclusion. ZIKV likely circulates silently in Nigeria, sustained by ecological and infrastructural factors. Fragmented vector control, inadequate diagnostics, and lack of integrated arboviral surveillance hinder timely recognition. Lessons from other Aedes-borne viruses should inform a more unified and proactive national strategy.
 317-323
317-323


ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Vpr, accessory protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (Retroviridae: Orthoretrovirinae: Lentivirus: Human immunodeficiency virus-1): features of genetic variants of the virus circulating in the Moscow region in 2019–2020
Abstract
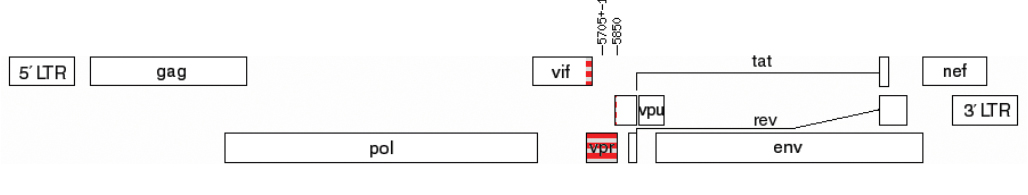
Introduction. Vpr is a multifunctional auxiliary HIV-1 protein. Oligomerisation is a prerequisite for the entry of Vpr into the virion and its subsequent participation in the early stages of HIV-infection. To date, natural amino acid substitutions in Vpr associated with disease progression were identified; the possibility of creating therapeutics based on Vpr is being considered.
The aim of the study is to investigate Vpr features in the most common genetic variants of HIV-1 circulating in the Moscow region in 2019–2020.
Materials and methods. HIV-1 samples obtained from 231 patients of the AIDS Prevention and Control Center in the period 2019–2020 were studied according to the scheme: proviral DNA extraction, amplification of the vpr gene, sequencing, and data analysis. Consensus Vpr sequences of the most common genetic variants in Russia and their spatial structures, variability of Vpr variants of HIV-1 sub-subtype A6 in patients with different stages of the disease were studied.
Results. Features of Vpr protein in different genetic variants of HIV-1 could influence the formation of their oligomeric forms. No sites with statistically significant differences in the frequency of amino acid substitutions were identified in patients with different stages of disease.
Conclusion. Vpr protein of HIV-1 genetic variants circulating in Russia may have differences in functional properties. Vpr-A6 variants had low variability in patients with different stages of the disease, and therefore Vpr-A6 can be considered as a target for the development of therapeutic agents.
 324-339
324-339


Modeling of mixed infection with Zika and West Nile viruses (Flaviviridae: Orthoflavivirus: Orthoflavivirus zikaense, Orthoflavivirus nilense) in vitro and in vivo
Abstract
Introduction. Mosquito-borne human diseases caused by Zika virus and West Nile virus (WNV) are widespread across multiple continents and cause major outbreaks. Their ranges overlap and the possibility of mixed infections is obvious. The information of such mixed infections is limited.
The aim of the study is to investigate the features of mixed infection of WNV and Zika virus in vitro and in vivo in order to assess their possible interference and/or enhancement of viral infection.
Materials and methods. The study used West Nile virus and Zika virus strains Vlg27924 and MR766, respectively. The infectious activity of viruses during mono- and co-infection was determined on Vero E6 cell culture using RT-PCR, as well as on BALB/c mice using various administration schemes.
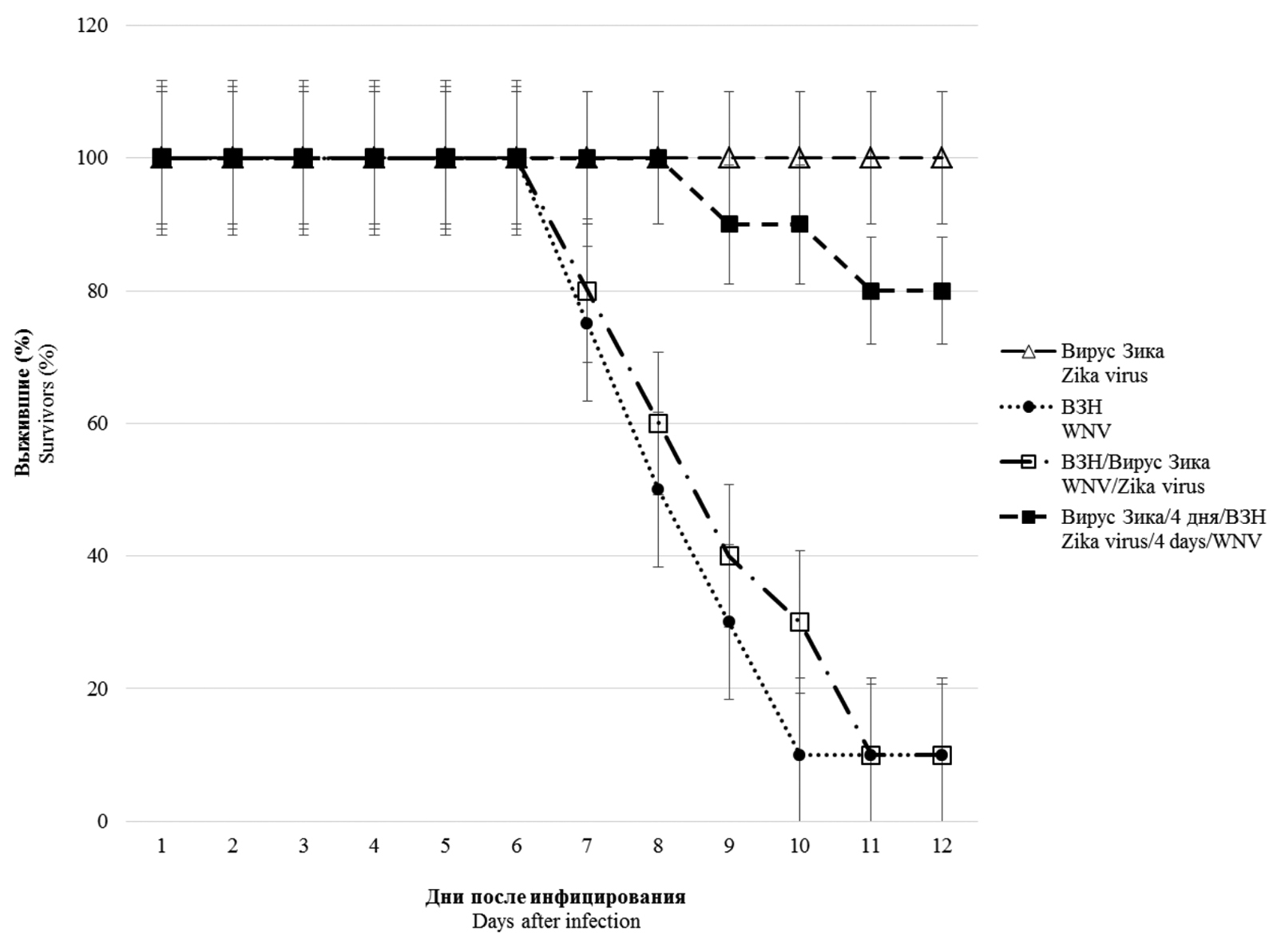
Results. In vitro studies of co-infection with WNV and Zika virus showed that co-infection leads to interference, with the degree of competitive inhibition of replication being more pronounced for Zika virus, reaching 1000 times or more when compared to mono-infection. During simultaneous infection in mice, Zika virus does not affect the development of lethal infection caused by WNV. However, preliminary (4 and 20 days) infection with a sublethal dose of Zika virus reliably protects animals from subsequent administration of 10 and 100 LD50 WNV, respectively. In pre-infected and co-infected animals with Zika virus, the development of WNV-specific viral neutralizing antibodies was recorded in higher titers than in WNV monoinfected animals.
Conclusion. The presence of in vitro interference between the studied orthoflaviviruses was shown, most pronounced in relation to the Zika virus. No significant effect was observed with simultaneous co-infection in vivo. However, pre-infection of mice with Zika virus provides protection to animals from lethal WNV infection due to the induction of high levels of antibodies that specifically neutralize its infectious activity.
 340-348
340-348


Endothelial protective properties of sacubitril-valsartan and drotaverine in influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 virus infection (Orthomyxoviridae: Alphainfluenzavirus: influenza A virus)
Abstract
Introduction. Severe influenza is characterized by damage and morphofunctional changes of the endothelium of blood vessels, which contributes to the development of hemorrhagic syndrome and can cause endothelial dysfunction. To optimize the pathogenetic therapy of influenza infection, a screening of medications with endothelial protective properties was carried out.
Aim. The aim of the study was to evaluate the endothelial protective properties of sacubitril/valsartan and drotaverine in influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 virus infection.
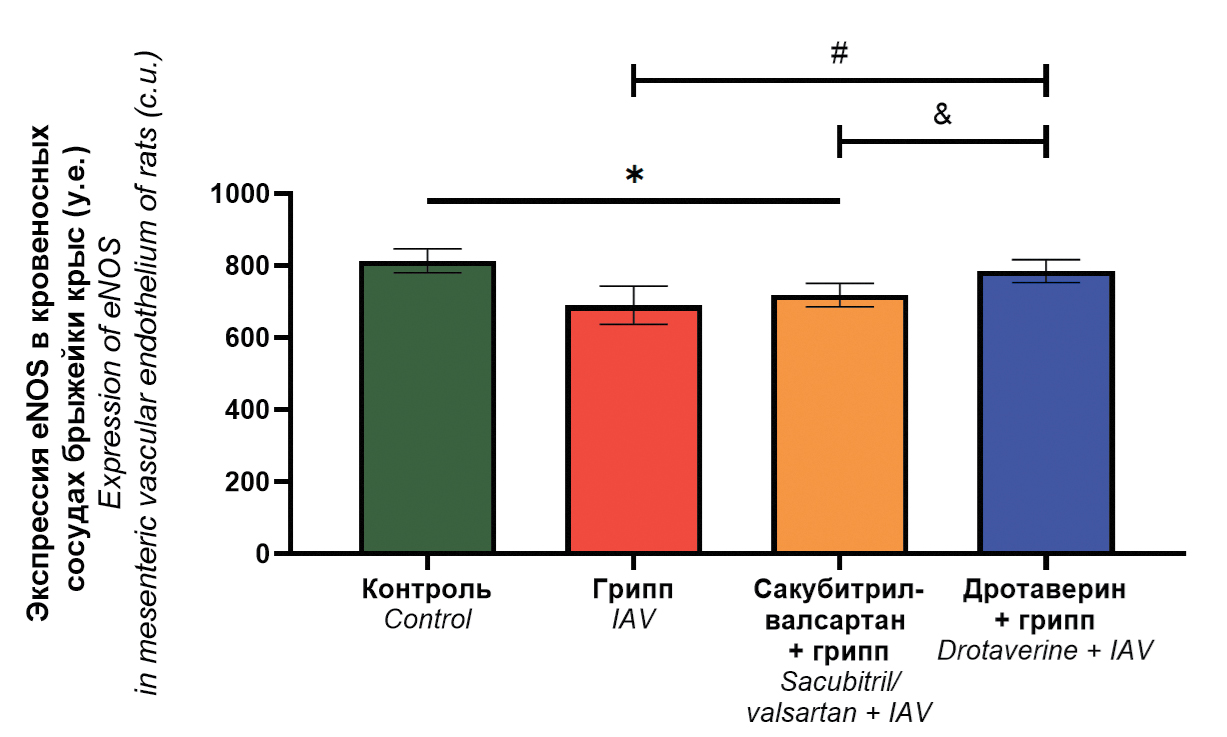
Materials and methods. The study was conducted on Wistar rats, which received sacubitril/valsartan and drotaverine (in treatment and prophylactic regimen) followed by intransal infection with influenza A/Saint-Petersburg/48/16 (H1N1)pdm09 virus. Rats without drug administration were included in the control group; rats received no medications followed by influenza virus infection – in challenge control group. The virus infectious activity was determined in pulmonary and mesenteric tissues. Vascular endothelium damage in lungs was assessed by three parameters (desquamation, morphological and dystrophic changes). Endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) expression level in endothelium of mesenteric blood vessels was determined as well as mesenteric arteries vasomotor activity.
Results. Drotaverine reduces the severity of histopathological changes in the pulmonary vascular endothelium; increases the maximal response of mesenteric blood vessels to acetylcholine compared to the infection control group; normalizes eNOS expression levels. Sacubitril/valsartan reduces the severity of desquamation in the pulmonary vascular endothelium; normalizes the response of mesenteric blood vessels to acetylcholine, while eNOS expression is decreased.
Conclusions. Drotaverine possesses more significant endothelial protective properties than sacubitril/valsartan when used in a treatment and prophylactic regimen in rats infected with influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 virus.
 349-362
349-362


NGS amplification panel HCV-seq for sequencing hepatitis C virus RNA (Flaviviridae: Hepacivirus)
Abstract
Introduction. Hepatitis C is a pressing global public health issue. The high variability of the hepatitis C virus (HCV) complicates its whole-genome sequencing; most studies sequence only specific regions of the genome. There is a need for a simple and reliable method for sequencing the whole genome of HCV.
Objective. Development and validation of NGS panel for whole-genome sequencing of HCV.
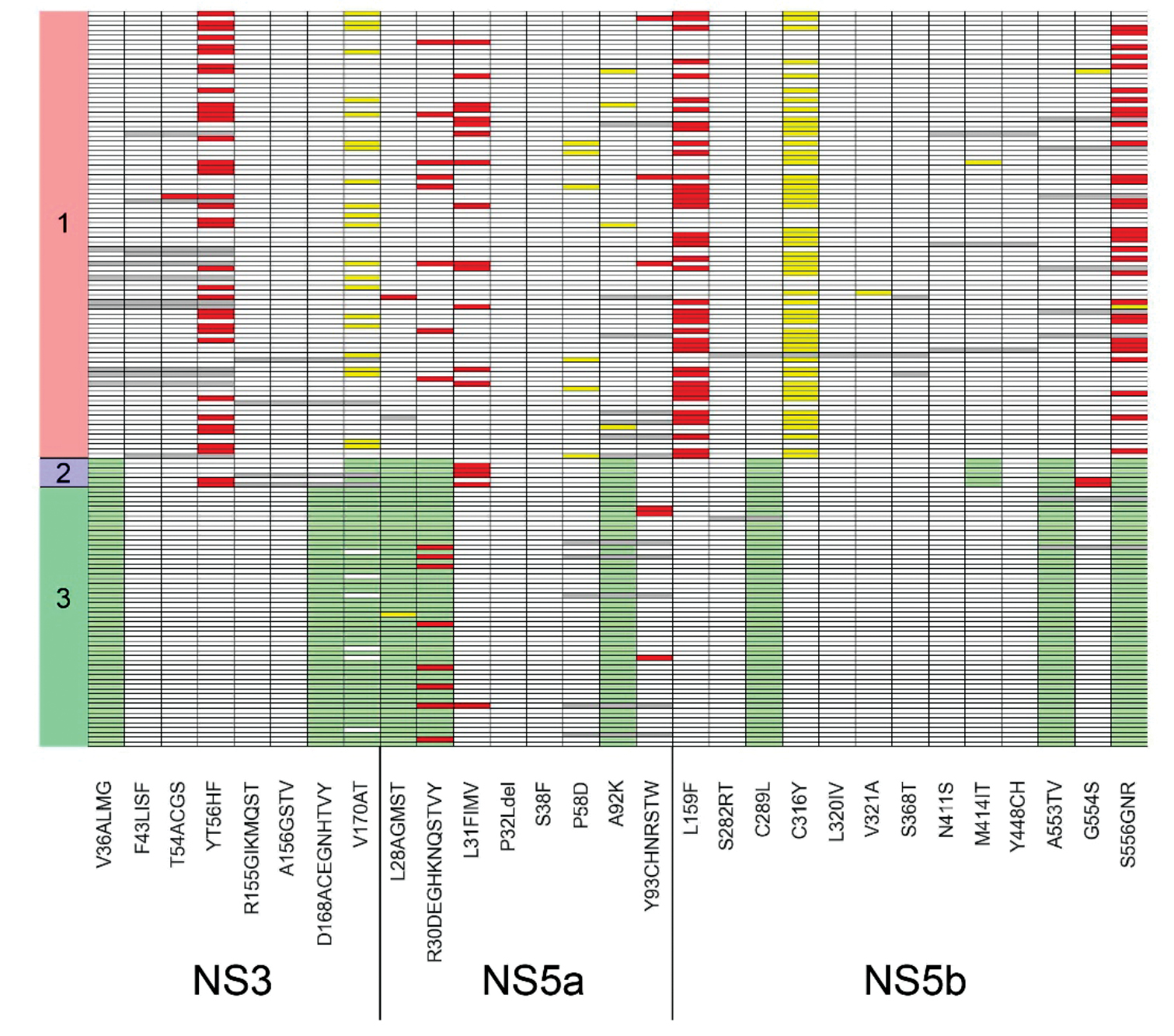
Materials and methods. This study presents NGS amplification panel for sequencing the genomes of HCV genotypes 1, 2, and 3. Depending on the genotype, a set of 79, 67, or 89 primers is used. These primers enable amplification of overlapping regions of the HCV genome.
Results. The panel was tested on 153 HCV RNA samples isolated from blood plasma specimens (93/6/54 samples of genotypes 1/2/3, respectively). Shannon entropy analysis showed that genetic heterogeneity within the E2 gene is significantly higher than in other parts of viral genome. The frequency of mutations associated with drug resistance was determined. Specifically, for genotype 1, the following mutation detection rates were observed in NS3: Y56F – 37.6%, V170I – 23.7%; in NS5a: R30Q – 8.6%, P58L/S/T – 6.5%, A92T – 4.3%; in NS5b: L159F – 45.2%, S556G/N – 33.3%.
Conclusion. The current study describes a method for whole-genome sequencing of HCV genotypes 1, 2, and 3. The HCV sequencing panel shows great potential for use in scientific research and epidemiological monitoring.
 363-373
363-373


TO VIROLOGIST’S AID
The results of certification of Pharmacopoeial standard for smallpox vaccine
Abstract
Introduction. Pharmacopoeial standard of activity, specificity and necrotic activity is used in testing of for smallpox vaccines. As a part of standard certification, an opportunity of using Pharmacopoeial standard for smallpox vaccine on new cell culture method (in vitro) for testing a new generation of smallpox vaccines was also defined.
The aim – certification of the Pharmacopoeial standard for smallpox vaccine to the main certified characteristics and defining an opportunity for using Pharmacopoeial standard for smallpox vaccine on new cell culture method (in vitro).
Materials and methods. Pharmacopoeial standard for smallpox vaccine (FSO 3.2.00113, series 130406) and pharmacopoeial biological methods described in the State Pharmacopoeia of the Russian Federation (S.Ph), the monograph 3.3.1.0033.15 Smallpox vaccine live were used in the study. For cell culture method, the technique from State Research Centre of Virology and Biotechnology «Vector» of the Federal Service for Surveillance in Consumer Rights Protection and Human Well-being, Novosibirsk Region, Koltsovo, Russian Federation was used. Statistical data were evaluated using Microsoft Excel software.
Results. The Pharmacopoeial standard for smallpox vaccine (FSO 3.2.00113) was certified. The possibility of using a new method of determining specific activity, specificity (identification) using the culture method was confirmed.
Conclusion. Along with the confirmation of certified characteristics, the possibility of using a new methodology for determining specific activity, specificity (identification) using the culture method was confirmed, and the main acceptance criteria were determined.
 374-387
374-387


SHORT COMMUNICATION
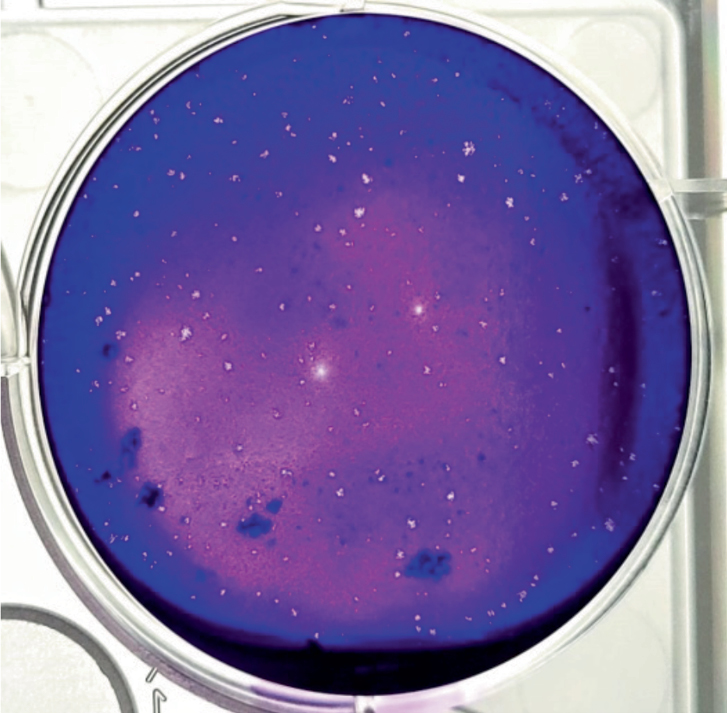
Detection of highly pathogenic orthopoxviruses (Poxviridae: Chordopoxvirinae: Orthopoxvirus) by dot immunoassay in a high-containment biological safety laboratory
Abstract
Introduction. Highly pathogenic for humans orthopoxviruses (OPV) – Variola virus (VARV) and Monkeypox virus (MPXV) can cause systemic diseases characterized by high contagiousness and often leading to death. In previous publications (https://doi.org/10.3390/v14112580), we reported on the development of a sensitive, rapid and easy-to-use immunochemical test potentially suitable for use in the infection foci and in laboratory conditions with a high level of biosecurity. The prototype of the diagnostic kit was tested on non-pathogenic and low-pathogenic for humans OPV and specifically detected them with a sensitivity within the range of 103 to 104 PFU/mL.
The aim of this work was to evaluate the sensitivity of this assay in detecting highly pathogenic for humans MPXV and VARV, as well as the applicability of the assay in a laboratory with a high level of biosafety (BSL-4).
Materials and methods. The efficiency of virus detection in cryolysates of CV-1 cell culture samples infected with VARV and MPXV was assessed using a one-step dot immunoassay method in a laboratory with biosafety level BSL-4.
Results. It was shown that the one-step dot assay allows detection of MPXV at a concentration of 2.5 × 103 PFU/mL, and VARV at a concentration of 1.0 × 104 PFU/mL. It was noted that vapors from disinfectants (hydrogen peroxide/formaldehyde) applied in biosafety cabinet decontamination may interfere with assay performance and affect result interpretation.
Conclusion. The one-step dot immunoassay can be performed in a BSL-4 laboratory. When limiting the contact of the detecting system with formaldehyde vapors, the sensitivity of the test for detection of VARV and MPXV falls within the previously declared range of 103–104 PFU/mL.
 388-392
388-392


ANNIVERSARY DATES
On the 80th anniversary of the birth of Oleg Ivanovich Kiselyov
 393-394
393-394