Vol 67, No 5 (2022)
- Year: 2022
- Published: 19.11.2022
- Articles: 8
- URL: https://virusjour.crie.ru/jour/issue/view/58
Full Issue
REVIEWS
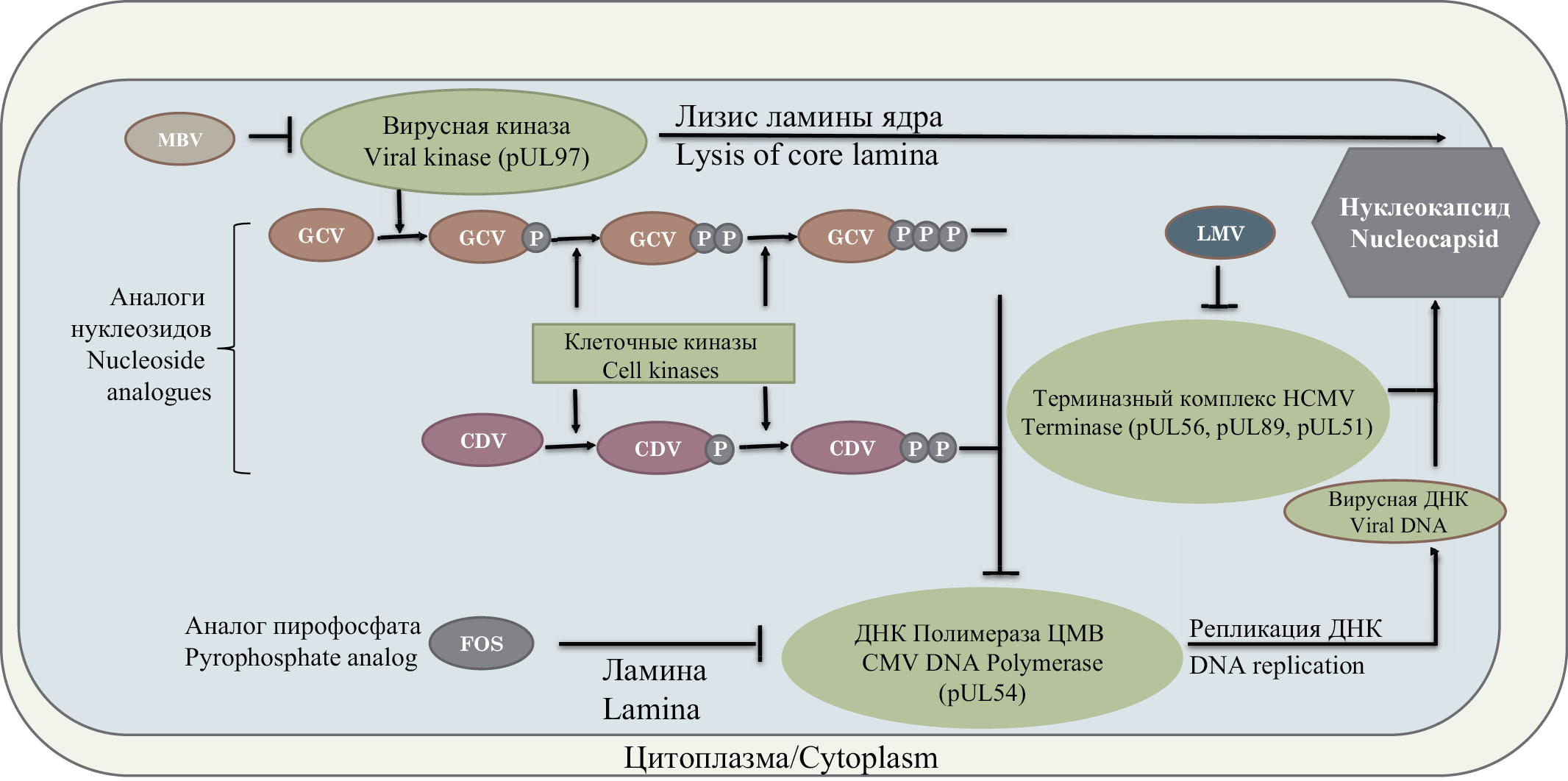
Resistance to antiviral drugs in human viruses from the subfamily Betaherpesvirinae
Abstract
The review provides information on the mechanisms of the emergence of resistance to antiviral drugs in human viruses from the subfamily Betaherpesvirinae. Data on the principles of action of antiviral drugs and their characteristics are given. The occurrence rates of viral resistance in various groups of patients is described and information about the possible consequences of the emergence of resistance to antiviral drugs is given. Information is provided regarding the virus genes in which mutations occur that lead to viral resistance, and a list of such mutations that have described so far is given. The significance of the study of mutations leading to the resistance of the virus to antiviral drugs for medical practice is discussed.
 385-394
385-394


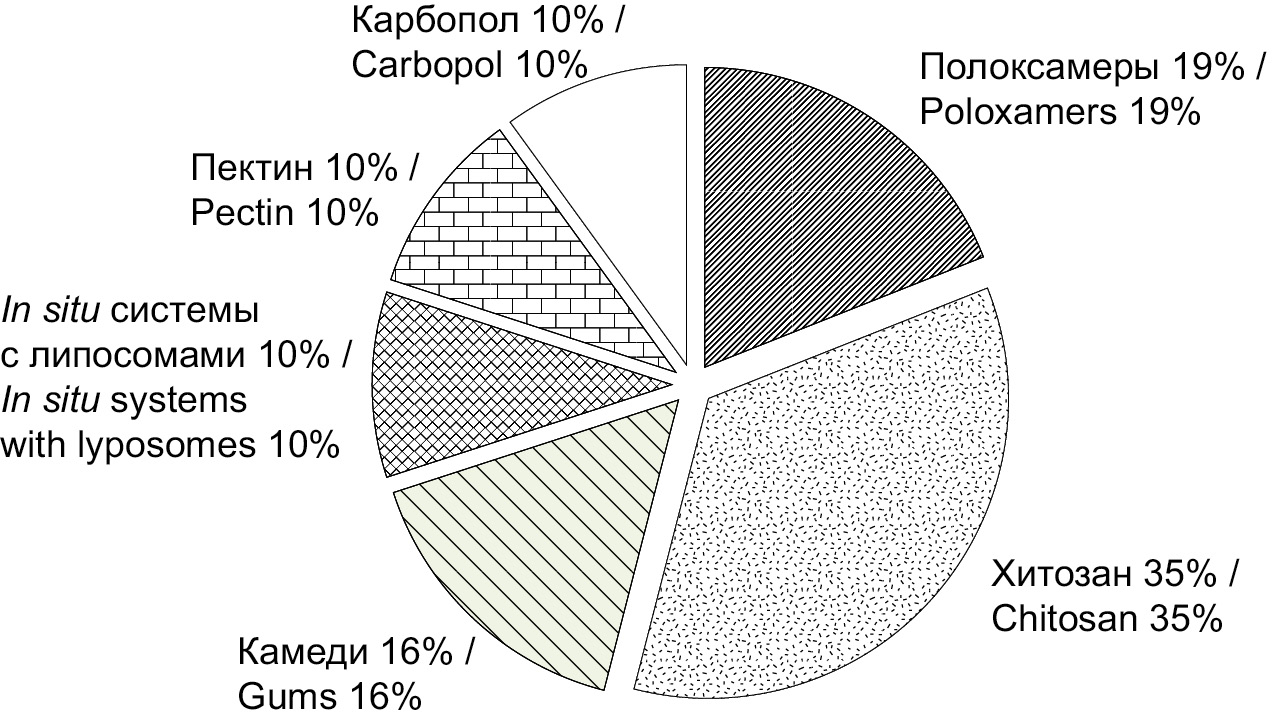
In situ gels as a modern method of intranasal vaccine delivery
Abstract
The continuous emergence of new pathogens and the evolution of microbial drug resistance make it absolutely necessary to develop innovative, effective vaccination strategies. Use of nasal vaccination can increase convenience, safety, cause both local and systemic immune reactions. Intranasal administration nevertheless has a number of shortcomings that can be overcome by using the latest achievements of pharmaceutical science. One of the aspects of such solution may be the use of systems for the production of intranasal vaccines in situ – polymer compositions that provide a directed sol-gel transition controlled by the physiological conditions of the nasal cavity. At the same time, the gelation of the administered dose in contact with the nasal mucosa involves prolonged exposure of the drug at the injection site, greater mucoadhesion, counteraction to mucociliary clearance, modified and more complete release. A number of both foreign and domestic manufacturers produces polymers such as chitosan, gums, polyoxyethylene and polyoxypropylene block copolymers (poloxamers, proxanols), carbomers. For effective pharmaceutical development of new intranasal IBD delivery systems corresponding to the QbD concept, not only the knowledge of the range of excipients is necessary, but also simple, accessible, and reproducible methods for determining indicators that define the critical parameters of such delivery systems. In accordance with the conducted scientific search, the main indicators of standardization of in situ intranasal systems were identified: temperature and time of gel formation, gel strength, rheological characteristics, mucoadhesion, release, nasal mucociliary clearance time.
 395-402
395-402


ORIGINAL RESEARCHES
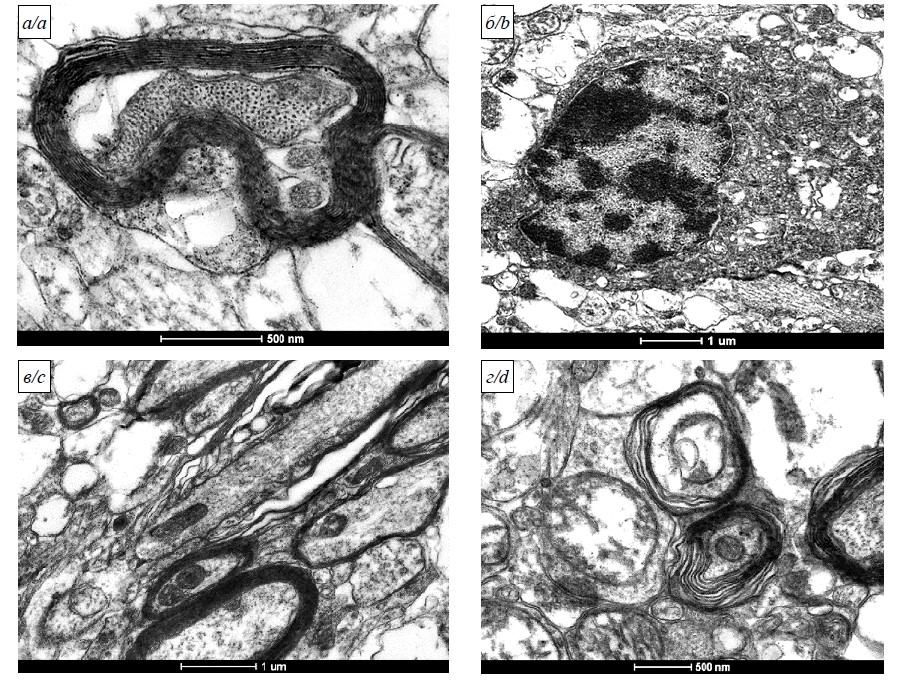
An electron microscopic study of neocortex of Syrian hamsters (Mesocricetus auratus) infected with SARS-CoV-2 (Coronaviridae: Coronavirinae: Betacoronavirus: Sarbecovirus)
Abstract
Introduction. Convalescent COVID-19 patients have various signs of central nervous system damage, including those directly associated with SARS-CoV-2. Hence, studies of SARS-COV-2 related morphological changes in neocortex are particularly relevant for understanding the mechanisms of their formation and development of approaches to preclinical evaluation of the effectiveness of antiviral drugs.
The purpose of the research is a longitudinal study of the ultrastructural alterations in Syrian hamsters’ neocortex after experimental SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Materials and methods. Male Syrian hamsters weighing 80–100 g, aged 4 to 6 weeks, were infected with 26 μl SARS-CoV-2 intranasally with 4×104 TCD50/ml of viral particles. The animals were euthanized on days 3, 7 or 28 post-infection, the brain was extracted with the cortex excision. The material analysis was performed using transmission electron microscopy.
Results and discussion. On day 3 post-infection, the number of moderately hyperchromic neurons in neocortex increased, while by the day 7 the number of apoptotic cells significantly increased. Simultaneously, an increased signs of neuronophagy and representation of atypical glia were observed. Increased number of altered oligodendrocytes was observed on day 28 post-infection. Viral invasion was accompanied by changes in neocortical cells since day 3 post-infection, such as transformation of their nucleus, the rough endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi vesicles as well as microvascular spasm with perivascular edema.
Conclusion. As a result of electron microscopic study, the ultrastructural alterations in neocortex were described in an experimental model of SARS-CoV-2 infection. The findings can be used to identify the mechanisms of infection pathogenesis and to search for the new directions in development of medicines.
 403-413
403-413


Quality analysis of a combined domestic vaccine for the prevention of measles, rubella and mumps
Abstract
Introduction. The need to maintain a high level of vaccination coverage against measles, rubella and mumps in conditions of an increased risk of outbreaks of infections due to violations of vaccination tactics associated with the pandemic of coronavirus infection and due to the unfavorable epidemic situation in neighboring countries determines the advisability of using a combined vaccine for the simultaneous prevention of these three socially significant infections.
The aim of the study: to analyze the quality of commercial series of a new domestic combined cultured live vaccine against measles, rubella and mumps (MRM) throughout the entire time of its manufacturing according to all specification indicators in regulatory documentation (RD).
Materials and methods. The object of the study was the combined cultured live vaccine against measles, rubella and mumps. The analysis of the quality of the drug was carried out according to 86 consolidated production protocols of manufactured series, as well as according to the results of control of these series in the Testing Center for Quality Expertise of the Federal State Budgetary Institution NCESMP of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation.
Results. It is shown that the quality of the combined drug for the prevention of measles, rubella and mumps corresponds to the RD in all studied indicators. The drug does not contain an antibiotic. Bovine serum albumin, which is a technological impurity, is detected in quantities more than 5 times lower than the established norm. A comparison of the specific activity of the viral components of new combined domestic vaccine and the components of the bivalent vaccine against measles and mumps produced by the company in 2019–2021 showed that the spread of the activity values of the viral components in the new drug and in the series of mumps-measles vaccine was minimal, which allowed us to make a conclusion about the stability of the production technology.
Conclusion. The quality of the new domestic combined vaccine for the prevention of measles, rubella and mumps meets WHO requirements. The results of the conducted studies indicate the stability of production and the standard quality of the drug. The use of a combined vaccine against three significant infections will ensure the necessary level of vaccination coverage in the population. Information about the results of studies can help reduce the number of vaccination refusal.
 414-422
414-422


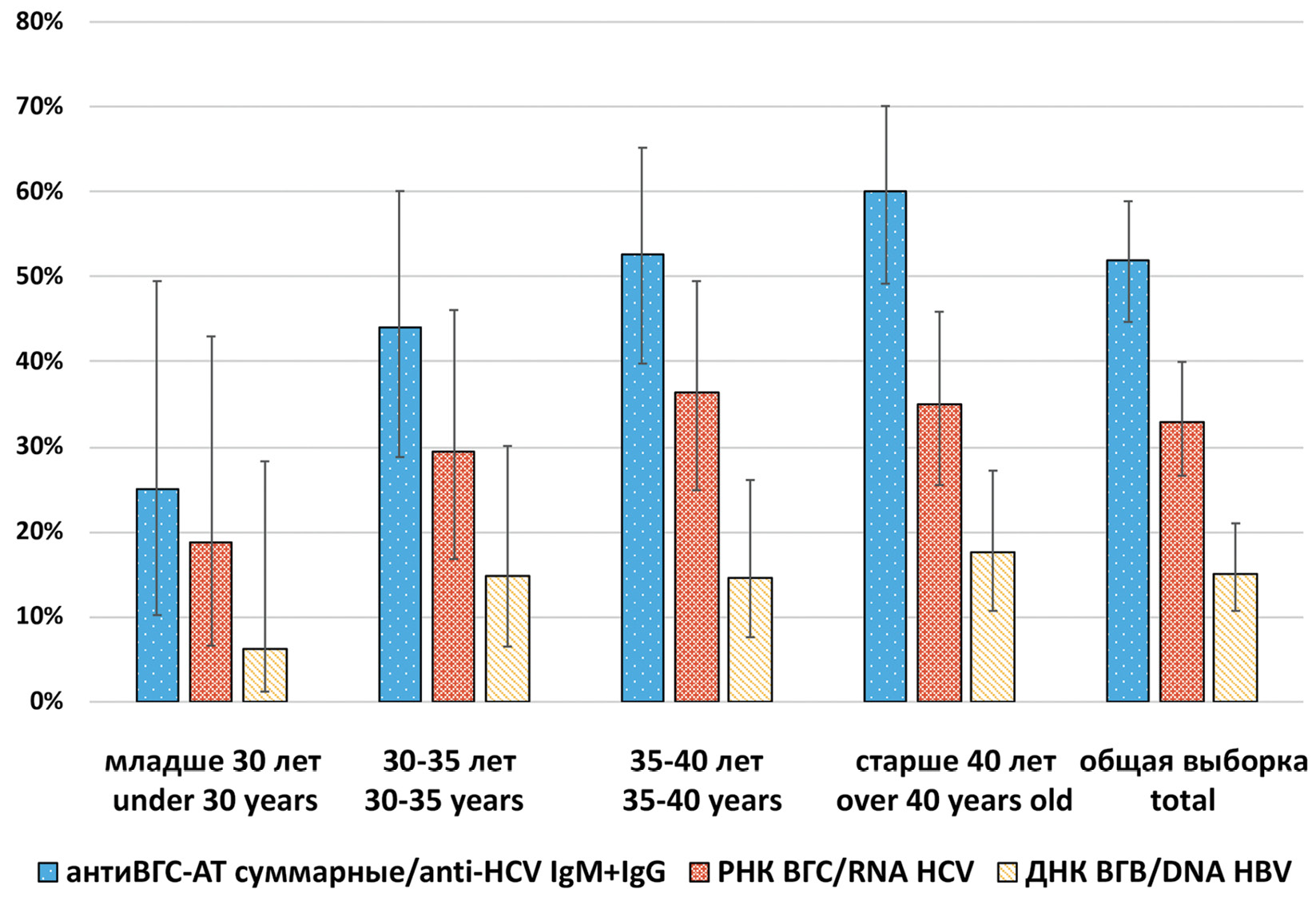
Prevalence and molecular genetic characteristics of parenteral hepatitis B, C and D viruses in HIV positive persons in the Novosibirsk region
Abstract
Introduction. Parenteral viral hepatitis (B, C, D) and HIV share modes of transmission and risk groups, in which the probability of infection with two or more of these viruses simultaneously is increased. Mutual worsening of the course of viral infections is important issue that occurs when HIV positive patients are coinfected with parenteral viral hepatitis.
The aim of the study was to determine the prevalence of HCV, HBV and HDV in HIV positive patients in the Novosibirsk region and to give molecular genetic characteristics of their isolates.
Materials and methods. Total 185 blood samples were tested for the presence of total antibodies to HCV, HCV RNA, HBV DNA and HDV RNA. The identified isolates were genotyped by amplification of the NS5B gene fragment for HCV, the polymerase gene for HBV and whole genome for HDV.
Results. The total antibodies to HCV were detected in 51.9% (95% CI: 44.7–58.9), HCV RNA was detected in 32.9% (95% CI: 26.6–39.5) of 185 studied samples. The distribution of HCV RNA positive cases completely repeated the distribution of HCV serological markers in different sex and age groups. The number of HCV infected among HIV positive patients increases with age. HCV subgenotypes distribution was as follows: 1b (52.5%), 3а (34.5%), 1а (11.5%), 2а (1.5%). 84.3% of detected HCV 1b isolates had C316N mutation associated with resistance to sofosbuvir and dasabuvir. The prevalence of HBV DNA in the studied samples was 15.2% (95% CI: 10.7–21.0). M204I mutation associated with resistance to lamivudine and telbivudine was identified in one HBV isolate. Two HDV isolates that belonged to genotype 1 were detected in HIV/HBV coinfected patients.
Conclusion. The data obtained confirm the higher prevalence of infection with parenteral viral hepatitis among people living with HIV in the Novosibirsk region compared to the general population of that region. The genetic diversity of these viruses among HIV infected individuals is similar to that observed in the general population.
 423-438
423-438


Comparative study of Wuhan-like and omicron-like variants of SARS-CoV-2 in experimental animal models
Abstract
Introduction. The variability of SARS-CoV-2 appeared to be higher than expected, the emergence of new variants raises concerns.
The aim of the work was to compare the pathogenicity of the Wuhan and BA.1.1/Omicron variants in BALB/c mice and Syrian hamsters.
Materials and methods. The study used strains of SARS-CoV-2: Dubrovka phylogenetically close to Wuhan-Hu-1, and LIA phylogenetically close to Omicron, BALB/c mice, transgenic mice B6.Cg-Tg(K18-ACE2)2Prlmn/HEMI Hemizygous for Tg(K18-ACE2)2Prlmn, Syrian golden hamsters. Animals were infected intranasally, pathogenicity was estimated by a complex of clinical, pathomorphological and virological methods.
Results. Comparative studies of SARS-CoV-2 Dubrovka and LIA strains on animal models demonstrated their heterogeneous pathogenicity. In parallel infection of BALB/c mice with Dubrovka and LIA variants, the infection proceeded without serious clinical signs and lung damage. Infection with the LIA strain resulted to a systemic disease with a high concentration of viral RNA in the lungs and brain tissues of animals. The presence of viral RNA in mice infected with the Dubrovka strain was transient and undetectable in the lungs by day 7 post-infection. Unlike the mouse model, in hamsters, the Dubrovka strain had a greater pathogenicity than the LIA strain. In hamsters infected with the Dubrovka strain lung lesions were more significant, and the virus spread through organs, in particular in brain tissue, was observed. In hamsters infected with the LIA strain virus was not detected in brain tissue.
Conclusion. The study of various variants of SARS-CoV-2 in species initially unsusceptible to SARS-CoV-2 infection is important for monitoring zoonotic reservoirs that increase the risk of spread of new variants in humans.
 439-449
439-449


TO VIROLOGIST’S AID
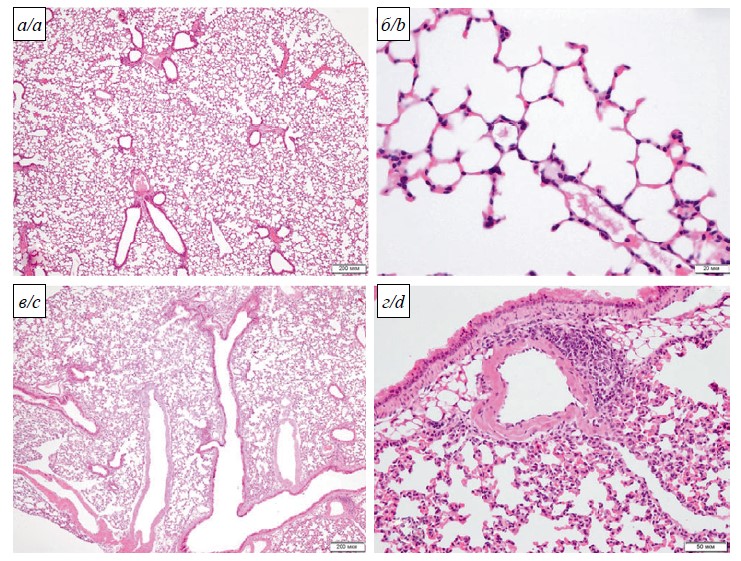
Adaptation of the sheep pox virus (Poxviridae: Capripoxvirus: Sheeppox virus) to African green monkey kidney cell line and evaluation of its immunobiological properties
Abstract
Introduction. Outbreaks of infectious diseases seriously hinder the preservation and increase of the number of small ruminants. Such infections include sheep pox virus (SPPV). According to the OIE data of 2021, SPP outbreaks were registered in countries such as Turkey, Israel, China, Maldives, Mongolia, Thailand, Russia, Algeria, Kenya, and in 2019 in Mangistau and Atyrau regions. In Kazakhstan annually conducts routine immunization of sheep at risk with a live attenuated vaccine produced by RIBSP.
Materials and methods. The object of the study was the vaccine strain of NISHI and the virulent strain A of the sheep pox virus. The virus was propagated in Vero cells. To determine the harmlessness and immunogenicity, sheep of the Kazakh fine-wool breed aged from 6 to 12 months were used. Virological, serological and immunobiological methods were used in the study.
Results. The results of the adaptation of the NISHI strain of SPPV to the Vero cell line are presented. Five passages in Vero cells resulted to the adaptation of the NISHI strain with the manifestation of a cytopathogenic effect specific to SPPV with a titer of 6.50 lg TCD50/ml. Following immunization, the formation of immunity was observed in animals on day 7 with an average protective titer 1.8 log2, which increased by day 21 to 4.33 log2.
Conclusion. It has been established that the NISHI strain of SPPV retains its virological and immunobiological properties during reproduction in a Vero cell line.
 450-458
450-458


EDITORIAL CONCEPT
130th anniversary of virology
Abstract
130 years ago, in 1892, our great compatriot Dmitry Iosifovich Ivanovsky (1864–1920) discovered a new type of pathogen – viruses. Viruses have existed since the birth of life on Earth and for more than three billion years, as the biosphere evolved, they are included in interpopulation interactions with representatives of all kingdoms of life: archaea, bacteria, protozoa, algae, fungi, plants, invertebrates, and vertebrates, including the Homo sapiens (Hominidae, Homininae).
Discovery of D.I. Ivanovsky laid the foundation for a new science – virology. The rapid development of virology in the 20th century was associated with the fight against emerging and reemerging infections, epidemics (epizootics) and pandemics (panzootics) of which posed a threat to national and global biosecurity (tick-borne and other encephalitis, hemorrhagic fevers, influenza, smallpox, poliomyelitis, HIV, parenteral hepatitis, coronaviral and other infections). Fundamental research on viruses created the basis for the development of effective methods of diagnostics, vaccine prophylaxis, and antiviral drugs. Russian virologists continue to occupy leading positions in some priority areas of modern virology in vaccinology, environmental studies oz zoonotic viruses, studies of viral evolution in various ecosystems, and several other areas. A meaningful combination of theoretical approaches to studying the evolution of viruses with innovative methods for studying their molecular genetic properties and the creation of new generations of vaccines and antiviral drugs on this basis will significantly reduce the consequences of future pandemics or panzootics. The review presents the main stages in the formation and development of virology as a science in Russia with an emphasis on the most significant achievements of soviet and Russian virologists in the fight against viral infectious diseases.
 357-384
357-384