Vol 70, No 5 (2025)
- Year: 2025
- Published: 15.11.2025
- Articles: 8
- URL: https://virusjour.crie.ru/jour/issue/view/142
Full Issue
EDITORIAL CONCEPT
Virus taxonomy and megataxonomy (Vira domain) – current status
Abstract
For nearly 80 years since the discovery of the first virus by the Russian scientist D.I. Ivanovsky, it has been recognized that all organisms of Earth’s biosphere serve as natural hosts for viruses. Viruses, grouped within the informal domain Vira, infect all three domains of cellular life: archaea – Archaea, bacteria – Bacteria, and eukaryotes – Eucarya (algae, fungi, protozoa, plants, invertebrates, and vertebrates). The formation of viral population gene pools through interactions with the gene pools of their hosts has taken place under changing environmental conditions over 3.5 billion years, giving rise to the vast diversity of the virosphere. The accumulation of data on the Earth’s virosphere, facilitated by the advent of high-throughput sequencing technologies (NGS), has necessitated a reassessment of approaches to virus classification and, since 2018, has led to a reform of viral taxonomy through the introduction of higher taxonomic ranks (megataxonomy). As of September 2025, the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) recognizes 15 taxonomic ranks for viruses, the most significant being: realm – 7, kingdom – 11, phylum – 23, class – 49, order – 93, family – 368, genus – 3769, and species – 16,215. Ongoing advances in metagenomics, metatranscriptomics, and the global ecology of the virosphere will inevitably drive further changes in viral taxonomy and megataxonomy. These developments are of fundamental importance for understanding the evolution of the biosphere and of practical relevance for developing new strategies to strengthen biological security and to mitigate the consequences of epidemic emergencies associated with emerging and reemerging infections.
 401-416
401-416


REVIEWS
Modern approaches to the construction and use of recombinant viruses
Abstract
The review describes certain viral vectors and considers various methods for constructing recombinant viruses with special attention paid to the homologous recombination and CRISPR/Cas9 system, and also describes the capabilities of using various cloning vectors (different plasmids, BAC etc.). The review also presents a comparative analysis of the effectiveness and safety of using various viral vectors, both for creating recombinant vaccines and for obtaining oncolytic viruses, as well as medicines for gene therapy.
 417-430
417-430


ORIGINAL RESEARCHES
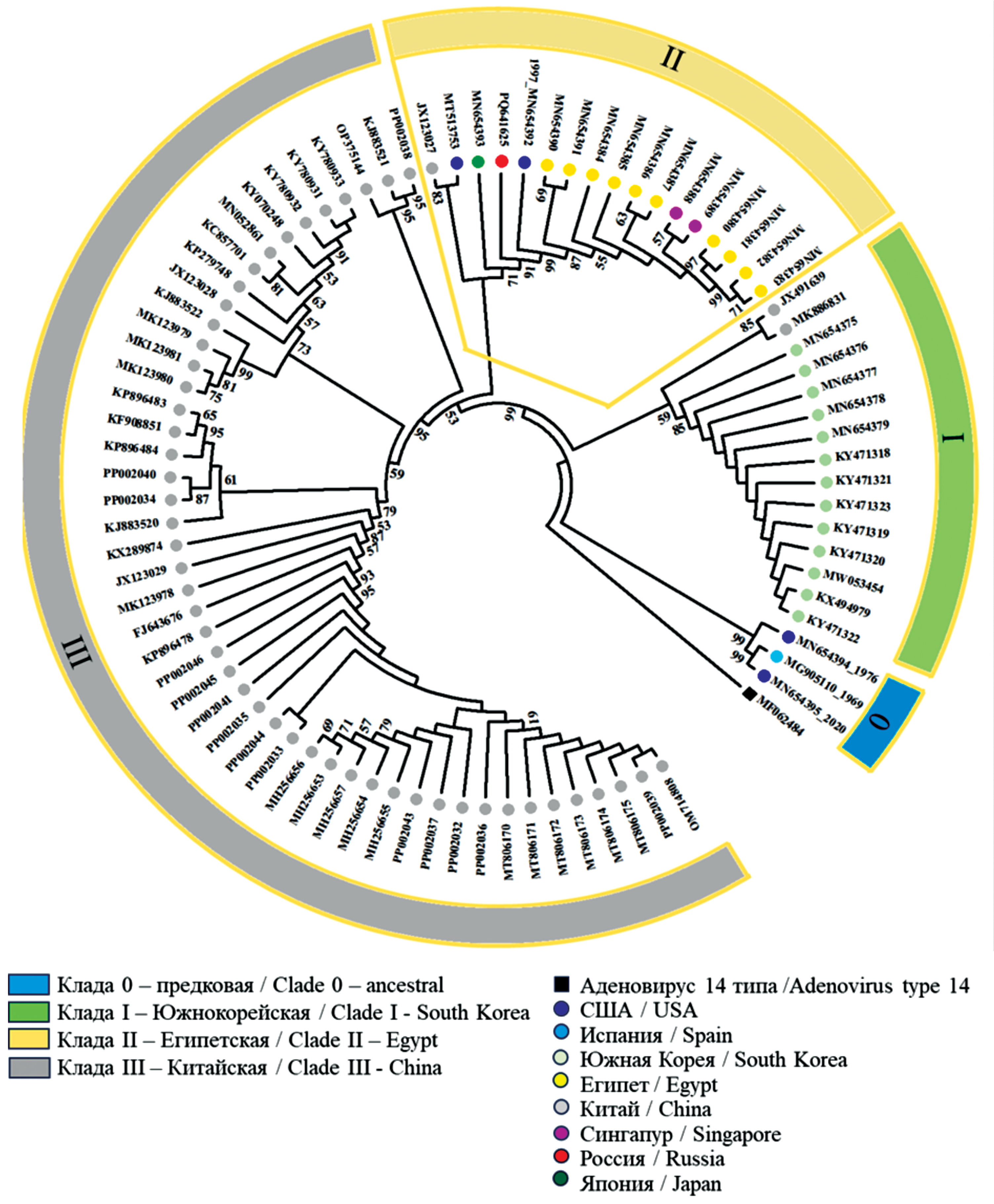
Genetic characteristics of the isolate of human adenovirus type 55 (Adenoviridae: Mastadenovirus) isolated in Moscow in 2022
Abstract
Introduction. Adenovirus infection occurs globally in the form of sporadic cases and isolated outbreaks. Human adenovirus type 55 (HAdV-55), endemic in China and South Korea, causes acute respiratory viral infections (ARVI) of varying severity, both among the civilian population and in military units in different countries of the world. Genomic research facilitates reliable identification of HAdV-55.
The aim of this study was to identify HAdV isolated in Moscow in 2022, as well as to conduct whole-genome sequencing and comparative genomic research.
Materials and methods. HAdV-55 was isolated from a sample of a patient hospitalized with pneumonia and analyzed using restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis and whole-genome sequencing. Bioinformatics comparative analysis was performed on a sample of sequences of 83 isolates.
Results. The whole-genome sequencing of first isolated in Russia HAdV-55 was conducted. The sequence of isolate SCV3008:Ad55 was deposited in GenBank (Accession Number PQ641625). Unique mutations in the SCV3008:Ad55 genome were identified, one of which resulted in a conservative T29A substitution in the penton that did not affect its functions. Phylogenetic analysis showed clustering of SCV3008:Ad55 with isolates of clade II, which included representatives of 7 countries on different continents, indicating a wide distribution of HAdV-55. Isolates from endemic regions of China and South Korea formed separate clades. The study of microsatellite length polymorphism in untranslated regions of the genome became an additional tool for distinguishing closely related genomes.
Conclusion. The obtained genomic information laid the foundation for further monitoring for HAdV-55 in Russia and demonstrated the informativeness and significance of whole-genome studies for monitoring adenoviruses. The development and implementation of genotyping methods aimed at detecting HAdV-55 and other clinically relevant genotypes will significantly improve the effectiveness of the diagnosis of adenovirus infections with the threat of developing bronchopneumonia.
 431-443
431-443


Resistance and chemosensitivity restoration in human cytomegalovirus-infected tumor cells to doxorubicin through combined treatment with aqueous fullerene dC60
Abstract
Introduction. Human cytomegalovirus infection can induce tumor cell resistance to chemotherapeutic agents through modulation of apoptotic pathways. In the search for alternative approaches to overcome virus-associated drug resistance, the application of nanomaterials (aqueous fullerene dC60) represents a promising strategy. The potential to overcome human cytomegalovirus mediated chemoresistance opens new avenues for developing combined therapeutic approaches in oncology.
Aim – to evaluate the impact of human cytomegalovirus infection on the resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma and promyelocytic leukemia cells to doxorubicin, as well as the potential of aqueous fullerene dC60 to restore chemosensitivity in monocytic leukemia cells.
Materials and methods. Hepatocellular carcinoma cells (Huh 7.5), promyelocytic leukemia cells (HL-60), monocytic leukemia cells (THP-1), and HCMV AD169 were used. The experimental procedures included standard cell culture techniques, virological methods, immunocytochemistry, Western blotting, Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction, Quantitative Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction and MTT assay.
Results. Human cytomegalovirus infection reduced doxorubicin cytotoxicity by 30% in both hepatocellular carcinoma and promyelocytic leukemia cells. In monocytic leukemia cells, combined treatment with doxorubicin and dC60 restored chemosensitivity to human cytomegalovirus infected cells, achieving 93% tumor cell death at half the standard doxorubicin concentration.
Conclusion. Human cytomegalovirus infection induces doxorubicin resistance in both hematopoietic (promyelocytic leukemia, monocytic leukemia) and solid (hepatocellular carcinoma) tumor models. Importantly, combined treatment doxorubicin with aqueous fullerene dC60 not only overcomes virus-mediated drug resistance in monocytic leukemia cells but also enhances cytotoxicity at reduced doxorubicin concentrations, offering prospects for developing less toxic combined therapeutic regimens.
 444-454
444-454


Hepatitis B and C viruses seroprevalence and risk factors among health care workers (HCWs) in referral hospitals in Brazzaville, Republic of Congo
Abstract
Introduction. Hepatitis B and C viruses cause chronic infections leading to liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma.
This study aimed to determine the seroprevalence of hepatitis B and C viruses and the potential risk factors which might influence the prevalence among health care workers (HCWs) in Brazzaville, Republic of Congo.
Materials and methods. We conducted a cross-sectional study from June to November 2022 among HCWs from the Talangaï and Makélékélé referral hospitals, Brazzaville. 107 HCWs were included and serological screening was carried out using rapid screening tests followed by the ELISA technique, after completing a survey questionnaire.
Results. The mean age was 36.56 ± 11.62 years with a female predominance of 1 : 0.36 sex ratio, laboratory technicians were the most represented socio-professional category. Seroprevalence of HBV was 7.48% and that of HCV was 3.74%. During their service, 40% have already been the victims of blood exposure accidents and have 7 times more risk of contracting HBV (odd ratio [OR] = 7.01 (95% Confidence interval [CI] 1.54–31.96); p = 0.01).
Conclusion. These data show that hepatitis B and C viruses are still endemic among HCWs in Republic of Congo. We can conclude that the health care sector is a high-risk profession due to infection with hepatitis B and C viruses. It is therefore necessary to improve the health and safety conditions of HCWs, implement new strategies to reduce occupational exposure to blood and body fluids, and reduce viral contamination by hepatitis B and C.
 455-462
455-462


Seroprevalence of Anti-Mpox Virus IgG Antibody and Awareness of Mpox Disease in Ibadan, Southwest Nigeria
Abstract
Purpose. Mpox cases were previously common in children; recent outbreaks of clade II have mostly affected young adults. Therefore, this study examines the knowledge, attitudes, and seroprevalence of the Mpox virus among consenting participants in Ibadan.
Materials and methods. Eligible individuals were those who voluntarily participated in the study and met the inclusion criteria specified for the study. A cross-sectional survey was conducted involving 94 respondents, investigating socio-demographic factors, awareness levels, attitudes toward prevention, and infection rates. The anti-Mpox virus IgG antibody was detected quantitatively using the Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) technique. The data were then analyzed using the χ2 test, while the antibody quantification was displayed with a Box and Whisker plot; statistical significance was determined at p < 0.05.
Results. The majority of respondents were female (66.7%) and aged 58 years and above (20.0%). Most had tertiary (40.0%) and secondary education (34.4%). Awareness of the Mpox was moderate, with 61.1% having heard of the virus, primarily through news (20.0%) and healthcare workers (18.9%). However, knowledge gaps were evident: only 38.9% recognized symptoms, and 40.0% understood modes of transmission. Attitudes towards prevention were generally positive; 60.0% believed Mpox could be prevented, and 73.3% were willing to take a vaccine. Still, readiness to engage in screening was low; 81.1% had never been tested, and 58.9% were unaware of local test availability. Regarding seroprevalence, females showed a significantly higher infection rate (27.4%) than males (9.6%) (χ2 = 3.854, p = 0.050). Age-wise, the highest infection rates occurred in those < 18 years (61.5%) and 53–57 years (66.6%) (χ2 = 30.817, p = 0.000), indicating significant age-related differences.
Conclusion. The findings highlight the need for targeted public health education, increased test access, and focused intervention strategies to improve Mpox virus prevention and control, especially among vulnerable age groups and under-informed populations.
 463-470
463-470


TO VIROLOGIST’S AID
Method for determining infectious and hemagglutinating titer of influenza A/Mallard Pennsylvania/10218/84 (H5N2) virus by changing the microviscosity of the viral membrane after interaction with phospholipid modifiers using cholesterol free liposomes as an example
Abstract
Introduction. The antiviral action of a number of drugs is associated with their modification of the lipid membrane of viruses. One of the possible mechanisms of such modification of the viral membrane is the extraction of cholesterol from the membranes of virions.
Objective of the study. A method has been developed for determining the infectious and hemagglutinating titer of avian influenza virus by changing the microviscosity of the viral membrane after incubation with phospholipid modifiers, using cholesterol-free liposomes consisting of phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylethanolamine in a molar ratio of 1 : 2 for 48 hours as an example.
Materials and methods. The extraction process was confirmed by two methods: gel filtration with radioactively labeled liposomes and virions, and by changing the polarization value of the fluorescent probe 1-anilinonaphthalene-8-sulfonate anion (8-ANS) in the viral membrane.
Results. A correlation was found between the change in infectious and hemagglutinating titer and the microviscosity of the viral membrane.
Conclusion. In this regard, it seems possible to use this dependence to determine the infectious and hemagglutinating activity of the influenza virus within one serotype in clinical laboratory diagnostics, using various fluorescent probes. It should be noted that not only liposomes of a certain composition can be used as lipophilic modifiers of the viral membrane, but also such compounds as ethylene glycol, erythritol, glycerol.
 471-476
471-476


Antibodies against VP3 protein of echovirus 30 (Picornaviridae: Enterovirus: Enterovirus betacoxsackie) neutralize virus in vitro
Abstract
Introduction. The widespread occurrence of enterovirus echovirus 30 (E30) and cases of severe disease indicate the need for vaccine development. Epitopes for neutralizing antibodies and T-cell response have been found in VP3 proteins of some enteroviruses. However, the immunogenic properties of VP3 E30 have not been studied. The aim of this work is to characterize the immunogenic properties of VP3 E30 and testing the virus-neutralizing properties of antibodies against VP3 E30.
Materials and methods. VP3E30 and the chimeric protein SN-VP3E30, consisting of the S region of norovirus VP1 and VP3 E30 were expressed in Escherichia coli. SN-VP3E30 was used to form virus-like particles (VLPs). The effect on human dendritic cells (DCs) was assessed by flow cytometry to measure changes in HLA-DR, CCR7, CD80, CD83 and CD86 expression. BALB/c mice and guinea pig were used for immunization with SN-VP3E30. Antibody titers and avidity were determined by ELISA. The interaction of antibodies with VP3 E30 was studied by immunoelectron microscopy and virus neutralization in embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma (RD) cell culture.
Results. Recombinant VP3 E30 caused incomplete DCs maturation, characterized by the understimulation of the CCR7 chemokine receptor expression. Inclusion of VP3 in the chimeric VLPs resulted in complete DCs maturation and a strong humoral immune response in laboratory animals. Antibodies against VP3 were characterized by high avidity, the ability to induce agglomeration of viral particles and neutralization of E30 in RD cell culture.
Conclusion. The obtained results indicate that VP3 can be used as an antigen in the composition of a subunit vaccine against enterovirus E30.
 477-486
477-486